Stroke recovery is a crucial phase that requires a comprehensive approach to regain as much function as possible and to live a full, active life. The road to recovery varies from person to person, depending on the severity and type of stroke, but rehabilitation plays a central role in the process. This blog provides detailed insights and practical tips for effective stroke recovery and rehabilitation.
Understanding Stroke and Its Impact
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. There are two main types of strokes: ischemic stroke, caused by blockages or narrowing of the arteries supplying blood to the brain, and hemorrhagic stroke, caused by blood vessels leaking or bursting. Recognizing stroke symptoms early and seeking immediate stroke treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Common stroke symptoms include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body, confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech, difficulty seeing in one or both eyes, difficulty walking, dizziness, loss of balance, or lack of coordination. Stroke symptoms in women can also include general weakness, disorientation, and fatigue.
The Importance of Rehabilitation
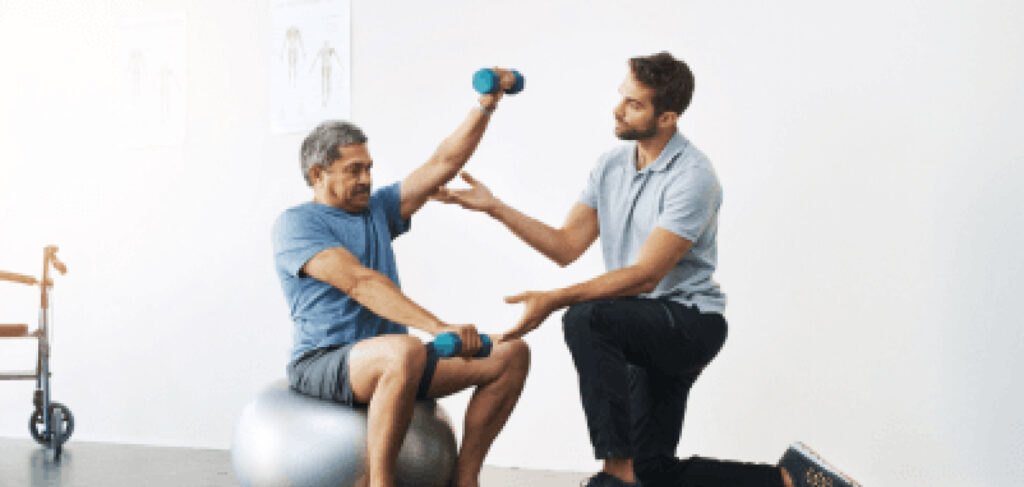
Rehabilitation is vital for stroke recovery. It helps stroke survivors relearn skills that are lost when part of the brain is damaged. Rehabilitation can also help improve overall health and prevent future strokes. The goals of stroke rehabilitation are to restore as much function as possible, achieve independence, and enhance the quality of life.
Early Intervention and Rehabilitation
Early rehabilitation is crucial and should begin as soon as possible, often within 24-48 hours after stroke treatment. This early start can help prevent complications such as blood clots, pneumonia, and muscle contractures.
Rehabilitation Settings
Rehabilitation can occur in various settings, depending on the severity of the stroke and the individual’s needs:
- Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities: Intensive therapy for those with significant impairments.
- Outpatient Rehabilitation: Less intensive therapy for those who are more independent.
- Home-Based Rehabilitation: For those who can function safely at home with or without caregiver support.

Effective Strategies for Stroke Recovery
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of stroke rehabilitation. It involves exercises to improve muscle strength, coordination, and range of motion. Techniques such as constraint-induced movement therapy, where the unaffected limb is restrained to encourage use of the affected limb, can be highly effective.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on helping stroke survivors perform daily activities such as dressing, eating, and bathing. Adaptive techniques and tools, like modified utensils and dressing aids, can enhance independence.
Speech and Language Therapy
For those with speech and language difficulties, therapy can improve communication skills. Exercises may include practicing sounds, words, and sentences, as well as using alternative communication methods such as picture boards.
Cognitive Rehabilitation
Cognitive rehabilitation addresses issues with memory, attention, problem-solving, and planning. Strategies may include memory aids like calendars and apps, mental exercises, and structured routines.
Emotional Support
Emotional well-being is critical in stroke recovery. Stroke survivors may experience depression, anxiety, and frustration. Psychological support, including counseling and support groups, can help manage these emotions.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is essential for stroke recovery and preventing future strokes. Key recommendations include:
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation is crucial as smoking significantly increases the risk of stroke.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Keeping conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol under control with medication and lifestyle changes.
Family and Caregiver Support
Family and caregivers play a crucial role in stroke recovery. They provide emotional support, assist with daily activities, and encourage adherence to rehabilitation programs. Caregivers should also seek support to manage their own stress and well-being.
Conclusion
Stroke recovery is a multifaceted journey that involves medical treatment, rehabilitation, lifestyle changes, and emotional support. By understanding the importance of early intervention and utilizing effective rehabilitation strategies, stroke survivors can maximize their recovery and improve their quality of life. Rehabilitation is a continuous process, and with the right support and determination, many stroke survivors achieve significant improvements and lead fulfilling lives.